Chat
What's a video call without being able to send messages to each other too? 100ms supports chat for every video/audio room you create.
Message Types
-
Broadcast messages are sent to Everyone in the chat
hmsSDK.sendBroadcastMessage. -
Direct messages are sent to a specific person
hmsSDK.sendDirectMessage. -
Group messages are sent to everyone with a particular
HMSRole. Such as allhostsor allteachersor allstudentshmsSDK.sendGroupMessage.- You can learn more about Templates and Roles here.
Sending Chat Messages
🔑 Note: The onMessage callback is not triggered for messages sent by the local peer. In other words, if you send a message yourself, you will not receive the onMessage callback for that particular message.
To ensure that the message sent by the local peer is included in your messages list, you will need to store it manually. You can achieve this by handling the onSuccess callback of the HMSActionResultListener and adding the message to your messages list, as shown in the example below.
Let's look at a simple implementation for chat methods:
class Meeting implements HMSUpdateListener, HMSActionResultListener{ ... // onMessage is HMSUpdateListener method called when a new message is received void onMessage({required HMSMessage message}) { //Here we will receive messages sent by other peers } void sendBroadcastMessage(String message,String type) { ///[message]: Message to be sent ///[type]: Message type(More about this at the end) ///[hmsActionResultListener]: instance of class implementing HMSActionResultListener //Here this is an instance of class that implements HMSActionResultListener, that is, Meeting hmsSDK.sendBroadcastMessage( message: message, type: type, hmsActionResultListener: this); } void sendDirectMessage(String message, HMSPeer peerTo,String type) async { ///[message]: Message to be sent ///[peerTo]: Peer to whom message needs to be sent ///[type]: Message type(More about this at the end) ///[hmsActionResultListener]: instance of class implementing HMSActionResultListener //Here this is an instance of class that implements HMSActionResultListener, that is, Meeting hmsSDK.sendDirectMessage( message: message, peerTo: peerTo, type: type, hmsActionResultListener: this); } void sendGroupMessage(String message, List<HMSRole> rolesToSendMessage,String type) async { ///[message]: Message to be sent ///[hmsRolesTo]: Roles to which this message needs to be sent ///[type]: Message type(More about this at the end) ///[hmsActionResultListener]: instance of class implementing HMSActionResultListener //Here this is an instance of class that implements HMSActionResultListener, that is, Meeting hmsSDK.sendGroupMessage( message: message, hmsRolesTo: rolesToSendMessage, type: type, hmsActionResultListener: this); } void onSuccess( {HMSActionResultListenerMethod methodType = HMSActionResultListenerMethod.unknown, Map<String, dynamic>? arguments}) { switch (methodType) { case HMSActionResultListenerMethod.sendBroadcastMessage: //Broadcast Message sent successfully //Add the message to messages list break; case HMSActionResultListenerMethod.sendGroupMessage: //Group Message sent successfully //Add the message to messages list break; case HMSActionResultListenerMethod.sendDirectMessage: //Direct Message sent successfully //Add the message to messages list break; ... } } void onException( {HMSActionResultListenerMethod methodType = HMSActionResultListenerMethod.unknown, Map<String, dynamic>? arguments, required HMSException hmsException}) { switch (methodType) { case HMSActionResultListenerMethod.sendBroadcastMessage: // Check the HMSException object for details about the error break; case HMSActionResultListenerMethod.sendGroupMessage: // Check the HMSException object for details about the error break; case HMSActionResultListenerMethod.sendDirectMessage: // Check the HMSException object for details about the error break; ... } } ... }
Now lets at each method one by one :
Sending Broadcast Messages
Want to let everyone in the chat know something? Call sendBroadcastMessage on the instance of HMSSDK to send a broadcast.
The parameters are:
- message: The text of the message.
- type[optional]: The type of the message, default is
chat. - hmsActionResultListener: An instance of
HMSActionResultListener.
💡 Note that the callback only lets you know if the server has received your request for the message or if there was some error.
It does not convey whether the message was delivered to or read by the recipient.
Also it's important to make a new callback per message because it will only contain the results of that particular call for sending a message.
hmsSDK.sendBroadcastMessage(message: "Hi", hmsActionResultListener: hmsActionResultListener);
Sending Direct Messages
Got secrets to share? Send a message directly to a single person with a direct message. Call sendDirectMessage on an instance of HMSSDK.
The parameters are:
- message: The text of the message.
- peerTo: The
HMSPeerinstance that should receive the message. - type[optional]: The type of the message, default is
chat. - hmsActionResultListener: An instance of
HMSActionResultListener.
💡 Note that the callback only lets you know if the server has received your request for the message or if there was some error.
It does not convey whether the message was delivered to or read by the recipient.
Also it's important to make a new callback per message because it will only contain the results of that particular call for sending a message.
hmsSDK.sendDirectMessage( message: "Hi", peerTo: peerTo, hmsActionResultListener: hmsActionResultListener);
Sending Group Messages
Need to call attention to all the hosts? All the teachers? All the developers? Call sendGroupMessage on an instance of HMSSDK.
The parameters are:
- message: The text of the message.
- hmsRolesTo: The list of
HMSRole, that is,the roles to whom the message needs to be sent. - type[optional]: The type of the message, default is
chat. - hmsActionResultListener: An instance of
HMSActionResultListener.
💡 Note that the callback only lets you know if the server has received your request for the message or if there was some error.
It does not convey whether the message was delivered to or read by the recipient.
Also it's important to make a new callback per message because it will only contain the results of that particular call for sending a message.
hmsSDK.sendGroupMessage(message: "Hi", hmsRolesTo: hmsRolesTo, hmsActionResultListener: hmsActionResultListener);
Receiving Chat Messages
When you called hmsSDK.join(config) to join a room, the HMSUpdateListener implementation that was passed in had the callback void onMessage({required HMSMessage message});.
This is where you'll receive new messages as HMSMessage during the call.
Let's look at what the HMSMessage class looks like:
class HMSMessage( final String messageId; final HMSPeer? sender; final String message; final String type; final DateTime time; HMSMessageRecipient? hmsMessageRecipient; HMSMessage({ required this.messageId, required this.sender, required this.message, required this.type, required this.time, this.hmsMessageRecipient }); )
- messageId: Id to uniquely identify the message
- message: Content of the text message or the text description of the raw message.
- type: Type of message sent. The default value is
chat. - hmsMessageRecipient: The intended recipient(s) of this message as a
HMSMessageRecipient. - time: DateTime of when the messaging server receives this message. This can be used for accurate ordering of your messages.
- sender: The
HMSPeerwho is sending this message.
Let's break down each parameter a bit more in detail :
Uniquely identifying the message
To uniquely identify a message, you can use the messageId field of HMSMessage. If the messageId is null then we set it as an empty string by default.
Identifying Senders:
The sender of a message is always contained in the sender field of HMSMessage. This lets you get the name and peer id of the sender.
Message Body:
The body of the message is in message as a String.
Time:
The time the message was sent is contained in time as a DateTime datatype.
Putting together a list of chat messages.
The UI is completely up to you to decide! You'll also need to hold onto all the received messages if you want to display history.
Identifying who the message was for
The HMSMessageRecipient contained in the hmsMessageRecipient field of HMSMessage lets you know who the message was for.
The HMSMessageRecipient contains:
class HMSMessageRecipient{ HMSPeer? recipientPeer; List<HMSRole>? recipientRoles; HMSMessageRecipientType hmsMessageRecipientType; }
recipientPeer: Only contains a peer when a specific single peer is being direct messaged.
recipientRoles: Only contains values when a group message is being sent to many roles.
hmsMessageRecipientType: Can contain enum values BROADCAST, PEER and ROLES.
-
HMSMessageRecipientType.BROADCASTfor a message being sent to everyone. If this is true, the other two fields will be null and empty respectively. -
HMSMessageRecipientType.PEERwill be set when it's a direct message. -
HMSMessageRecipientType.ROLESwill be set when it's a message to one or many roles.
Store Chat Messages
You can store chat message by creating a list of HMSMessage and append new messages from the callback onMessage({required HMSMessage message}) as follow:
List<HMSMessage> messages = []; void onMessage({required HMSMessage message}) { messages.add(message); }
Filter Chat Messages
You can filter chat messages by creating a separate list of HMSMessage.
List<HMSMessage> broadcastList = []; List<HMSMessage> rolesList = []; List<HMSMessage> peerList = []; List<HMSMessage> messageFilter(List<HMSMessage> messages, HMSMessageRecipientType type) { filterList = []; for(HMSMessage message in messages) { // Filter list based on Broadcast chat. if(message.hmsMessageRecipient.hmsMessageRecipientType == HMSMessageRecipientType.BROADCAST) { broadcastList.add(message); } // Filter list based on Roles chat(group messages). if(message.hmsMessageRecipient.hmsMessageRecipientType == HMSMessageRecipientType.ROLES) { rolesList.add(message); } // Filter list based on Peer chat(direct messages). if(message.hmsMessageRecipient.hmsMessageRecipientType == HMSMessageRecipientType.PEER) { peerList.add(message); } } }
Advanced Use-Cases
Sometimes the app requires to show messages in different styles. Something similar to this:
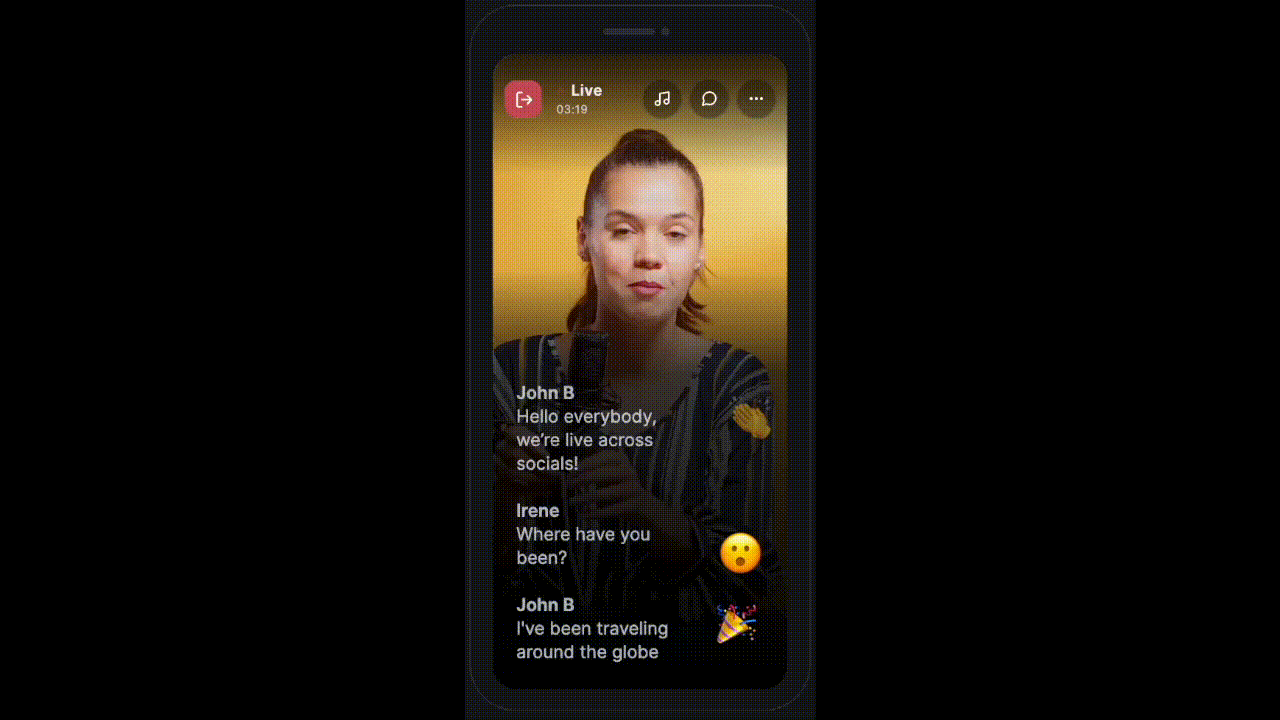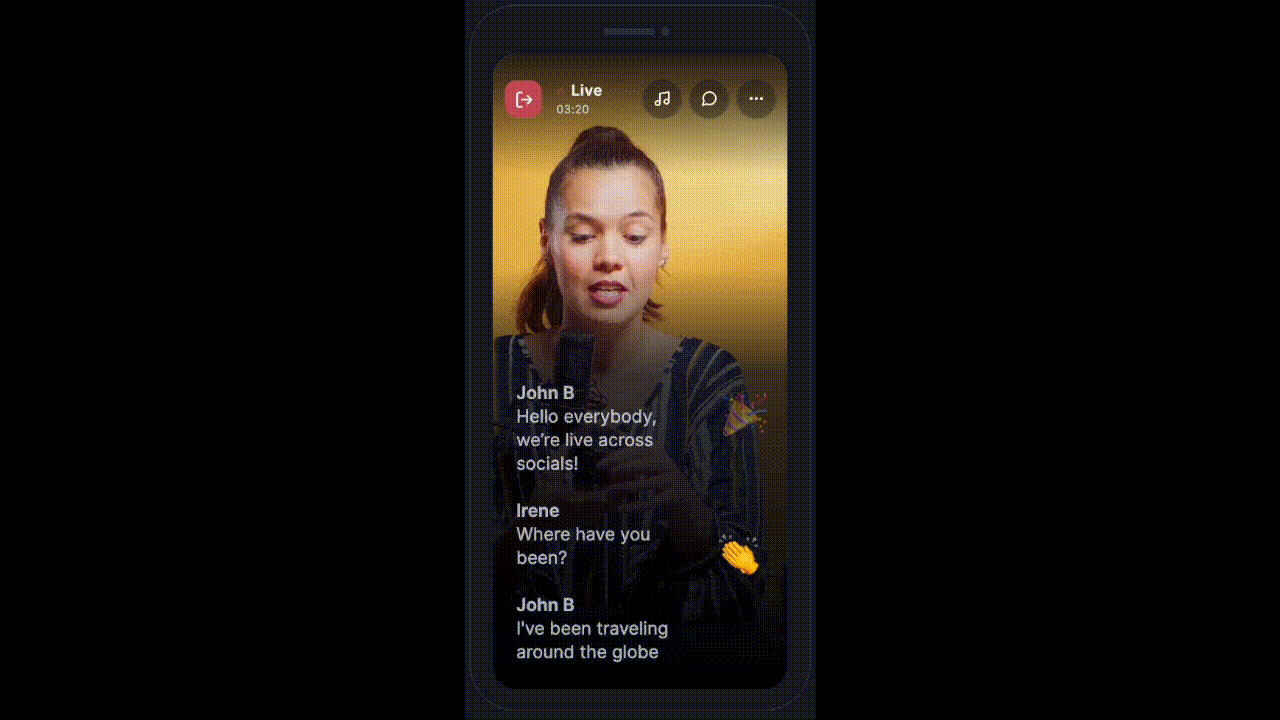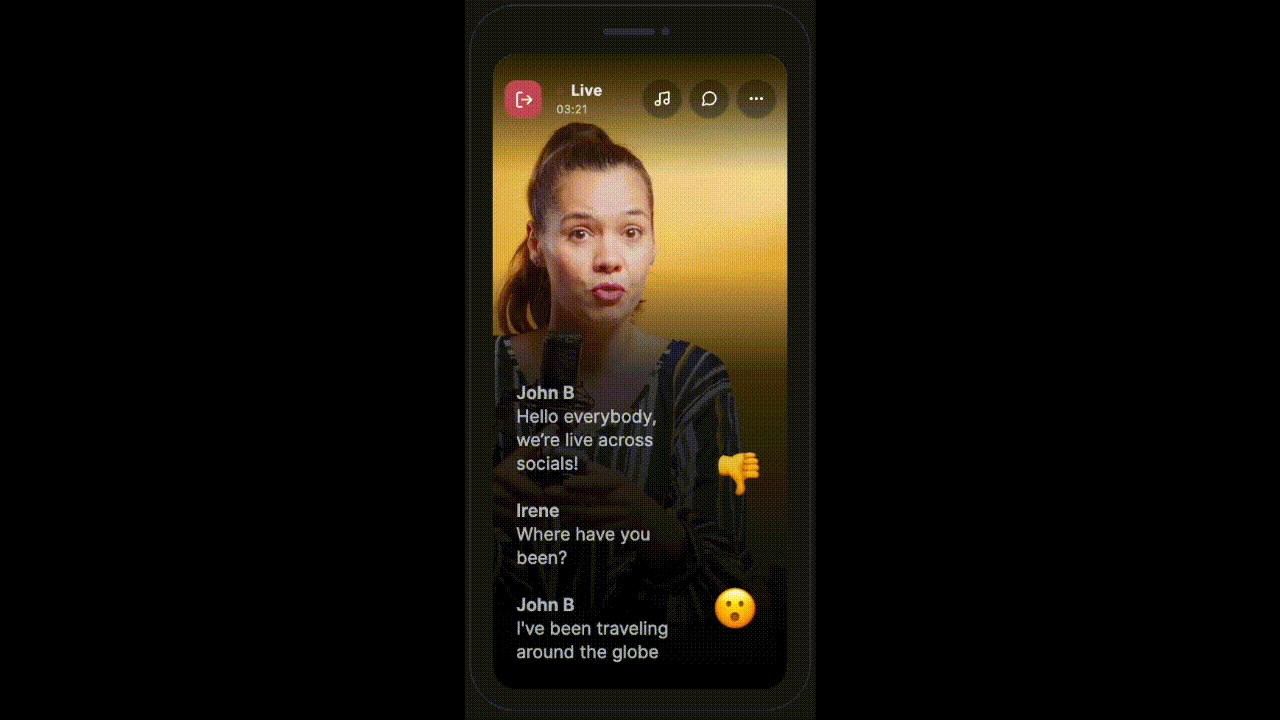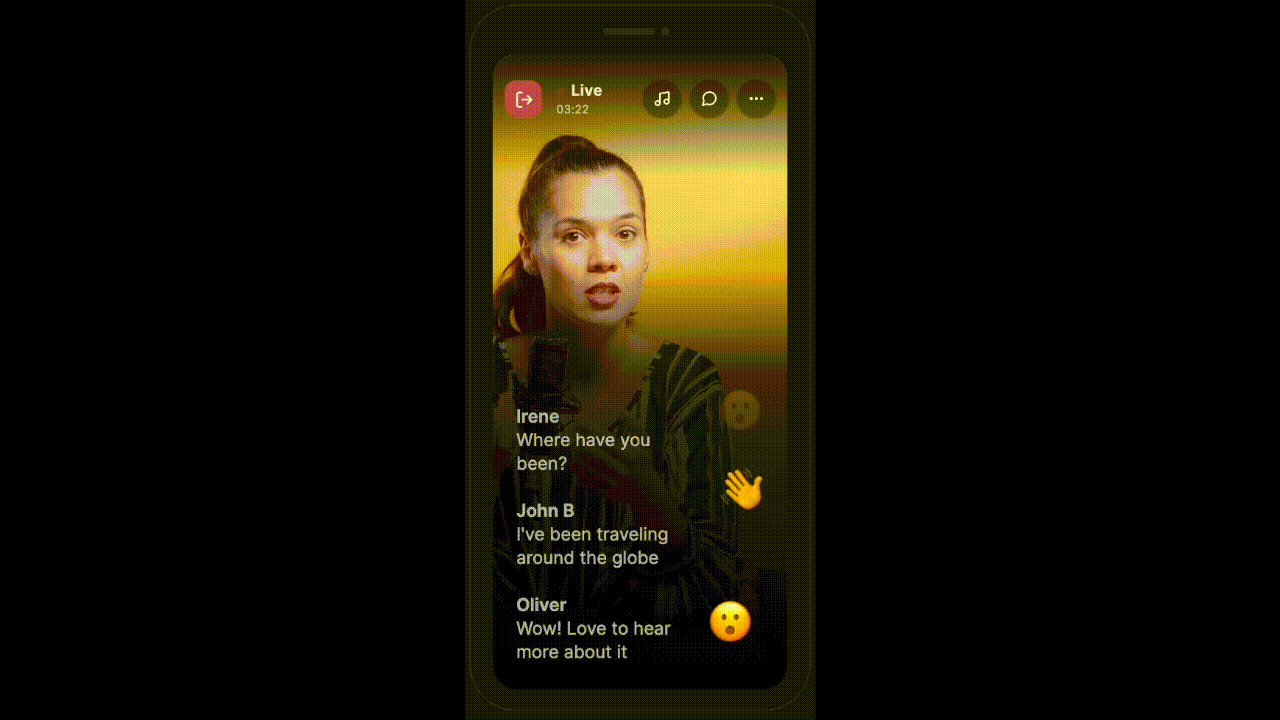
HMSSDK provides the type parameter of the HMSMessage object to take care of such use cases.
You can send messages as:
hmsSDK.sendBroadcastMessage(message: "😁", type: "emoji", hmsActionResultListener: hmsActionResultListener);
Filter out the messages based on the type parameter and handle the UI accordingly.
//Example to show emoticons when the message type is set to `emoji` void onMessage({required HMSMessage message}) { if(message.type=="emoji"){ //Show as emoticons on UI } else{ //Handle other cases } }



